CRM Data Quality (CDQ)
CDQ cleans large contact databases by finding complex patterns of duplicate data, achieves single version of truth through its Entity Resolution algorithms and executes real-time de-duplication checks on applications within the enterprise. |
Main FeaturesAssimilate data from multiple files and systems CDQ enables a data dictionary to be defined using the field constructor option. Hundreds of fields can be defined about the contact data which can be strings, numeric, text or date types. This definition can be modified at any time. Data can be uploaded from Comma Separated Values (CSV) or text files. The upload feature automatically attempts to map the incoming data to the fields in the data dictionary. Fields can be re-mapped or skipped if needed. Dozens of encoding options are available during import, with UTF-8 selected by default. During the import process, checks are performed on the completeness of data. The data can be added to an existing dataset or by default a new one will be created after a successful upload. External data can also be imported by connecting to applications like Salesforce, Eloqua and Zoho CRM. Any system with an API access can be integrated to CDQ. Create single contact records from disconnected datasets Data from multiple datasets can be merged after a common factor between them has been discovered by CDQ. Using its de-duplication rules, CDQ forms a cluster of records with this common criteria. These records can then be collapsed into a single golden record. The data custodian can do this merging manually or instruct CDQ to perform it automatically.
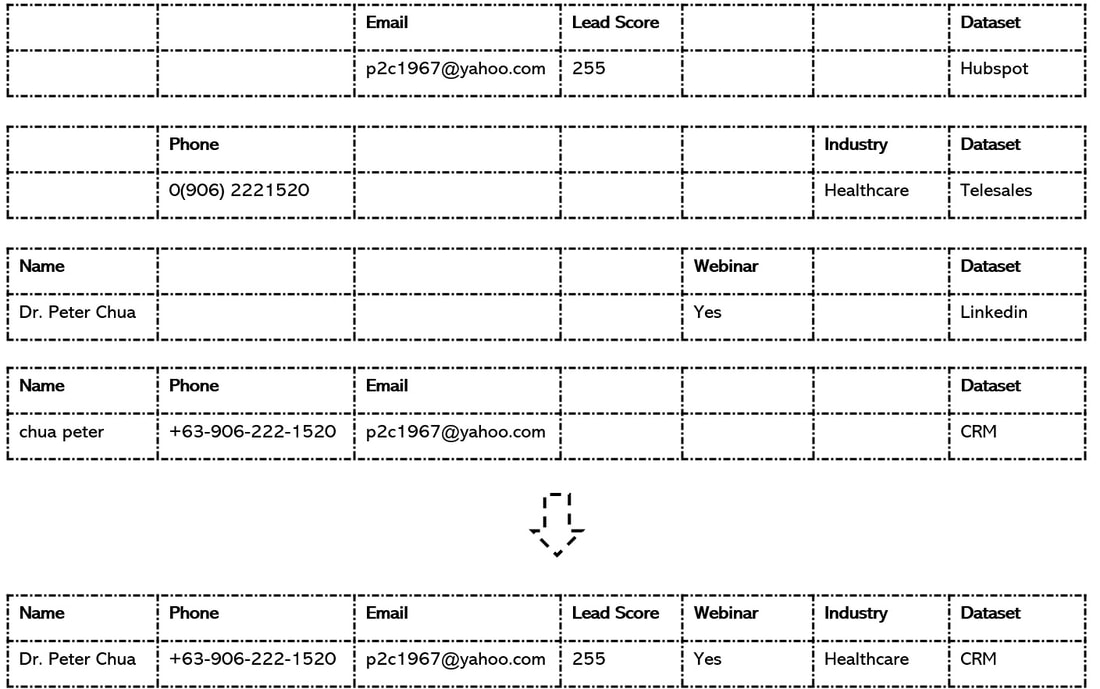
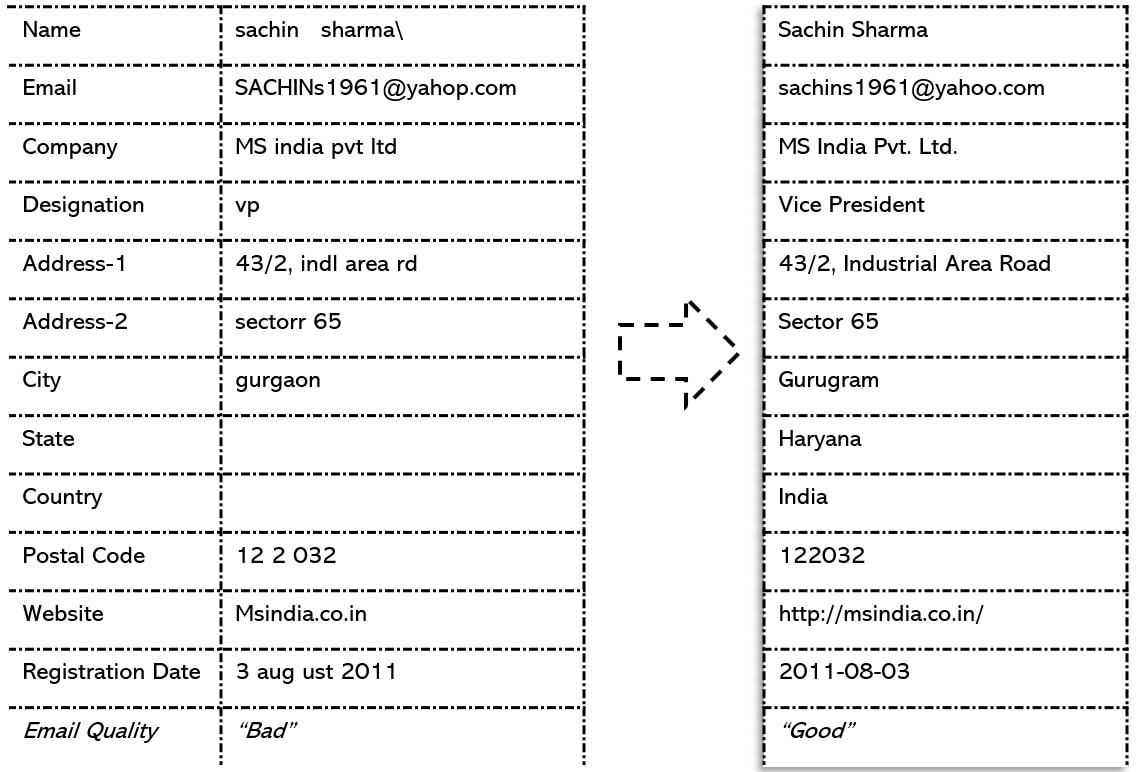
The following example will make it clearer. CDQ has found 4 common records which have been collapsed into a single golden record within CRM by the data custodian. Identify duplicate records across databases Using its pattern matching algorithms, CDQ can find common records across databases and multiple datasets. While the CSV and text files is usually directly uploaded into a dataset within CDQ , the data from external systems can be configured by either importing into CDQ or by storing the indexed keys of the records of that database. Storing the data within CDQ is optional. Essentially, it stores the key which it constructs after indexing the datasets. An external data system can be indexed by CDQ and that would be sufficient for it to compare that database with others or perform a real-time de-duplication on it. Automatically standardize, enhance and repair data CDQ has dozens of functions to manually or automatically repair, standardize and enhance the data within its datasets. The strength of these functions is shown in the example below in which an incoming record on the left is passed through them, resulting in the final record on the right.
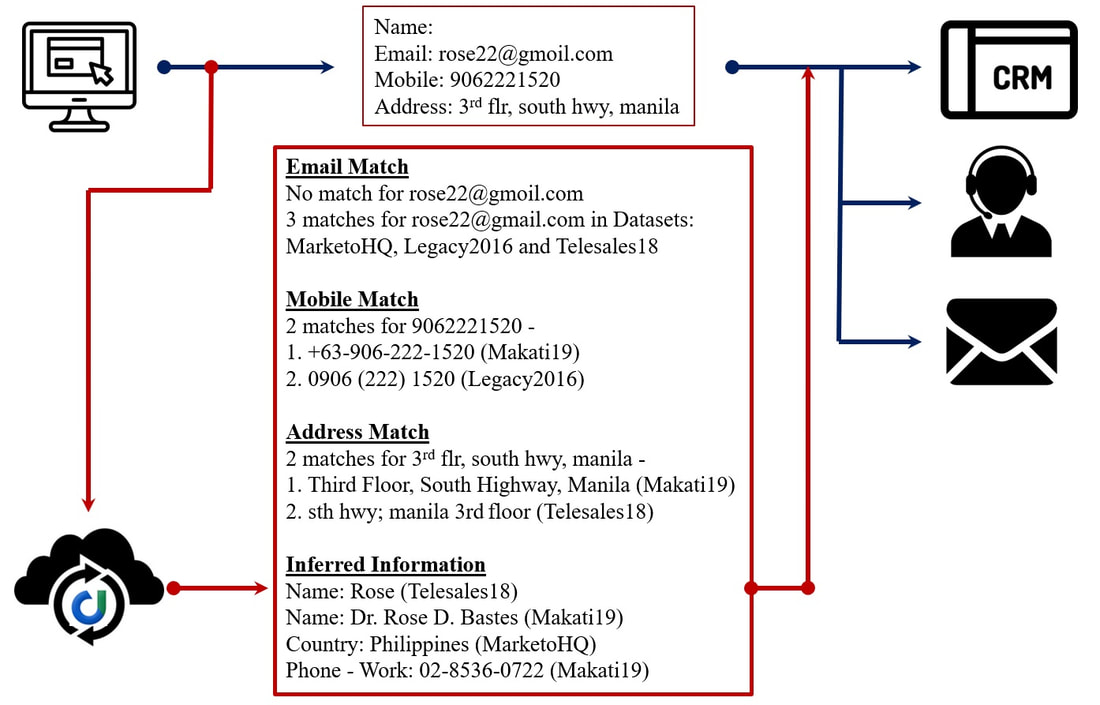
Check for duplicates in real-time from millions of records CDQ can find duplicates within seconds, across tens of millions of records. This de-duplication in real-time is being used by our customers from data entry to identification and in other innovative ways like explained in the example below:
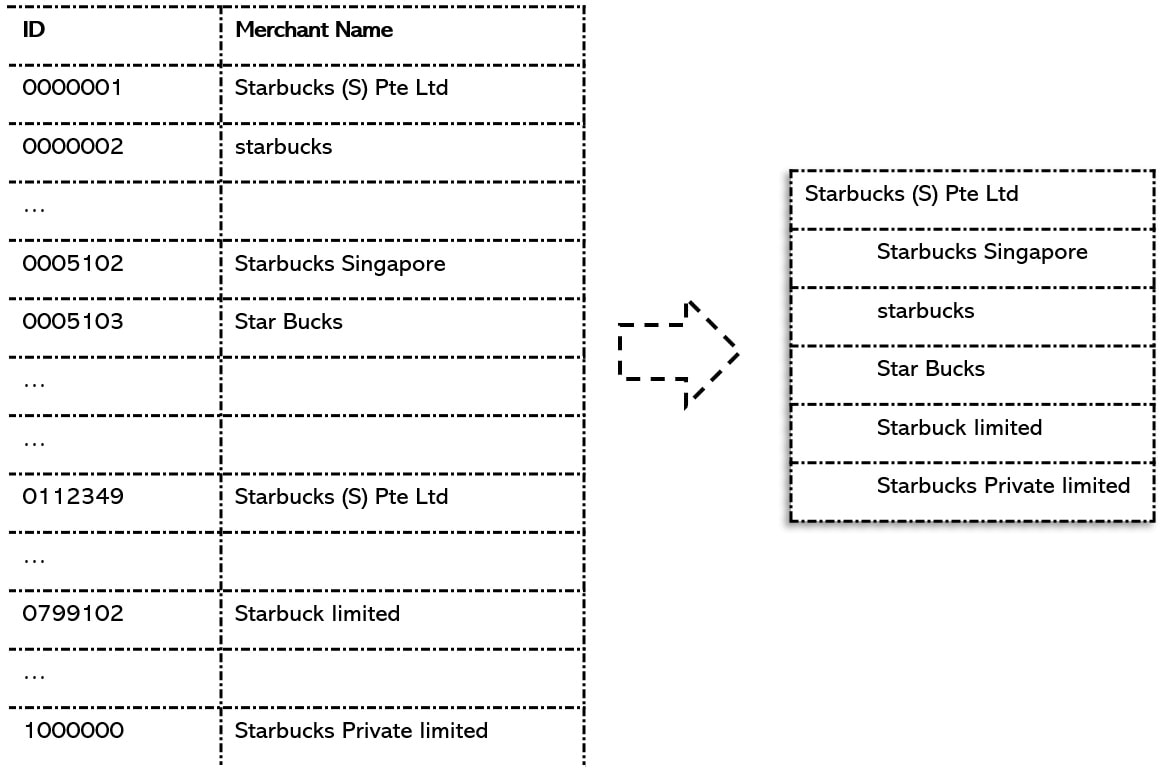
Before CDQ integration, the data is coming from a customer's web submission form and is being passed to CRM, telesales or lead-nurturing programs. In example above, CDQ is made to tap into this email (without integration) and it starts to perform the de-duplication for incoming records in real-time and sends that information to telesales. The actions (and their effectiveness) on original mail as compared to one sent by CDQ become very different. Resolve entity names and cluster within large bulk files From merchant data records in banks to epidemiological data in hospitals and product descriptions in warranty management, large files with millions of records need to be quickly resolved to determine the right entity to be used through some agreed logic.
In the example above, a million records are received in text file by a financial institution comprising of merchant names. CDQ can take this entire data set and provide an entity resolution map within an hour about identity of the main entity and which other records in the incoming file correspond to that entity. Here, CDQ shows (based on configured rules) that Starbucks (S) Pte Ltd is the main entity and the 5 other names should correspond to this main record within the text file. With this resolution, the file can now be easily processed. Merge duplicate contact records automatically or manually Finding the duplicate records is part of the solution, merging them into a single version of truth is the next step. Once the cluster of duplicate records is found, it is important to determine the master record which will lead the merging process. CDQ has a rich set of configurable rules to determine which record would be the master record within a cluster. The user can always over-ride this suggestion. What happens to the records which get merged can be configured too. They can get deleted or moved to a special data set to be analyzed later. Then there are values that can get overwritten or ones which get appended. Lastly, the merging process itself can be automatic and CDQ can take responsibility of determining the master record and merge duplicate records of tens of thousands of clusters into their master record within an hour. Examples of Duplicate ClustersCDQ extracts clusters of duplicate records from single or multiple datasets, which could comprise of millions of records. Here are some examples. Majority of them are close to real cases of duplicate data found by the product during its usage. The real data has been changed for confidentiality, but the discovered pattern is intact.
Full Name - First Example Example of Name de-duplication taken from a medical institution in India. Combination of salutations, qualifications and swap of first name and surnames were considered by CDQ :
Full Name - Second Example Example of Name de-duplication taken from a warranty registration database in Philippines:
Full Name - Third Example A powerful example of CDQ's capabilities. Example of Name de-duplication taken from a database of a South Asian country:
Full Name - Fourth Example Example of variations of a name considered in a suspected duplicate cluster by CDQ:
Address - First Example This is one of the best example of Address de-duplication, highlighted by CDQ within a massive CRM database in India. Not only there are inconsistent abbreviations and spelling errors, the old and new official name of the city has been detected as duplicate:
Address - Second Example An example of Address de-duplication, from Singapore:
Address - Third Example An example of duplicate address cluster from Australia. Note the abbreviations and variations of state name captured in duplicate cluster:
Mobile Numbers CDQ finds mobile numbers in multiple formats and groups the duplicate together. Here's an example of such a group:
Company Name - First Example An example of Company Name de-duplication, from India:
Company Name - Second Example Another similar example of Company Name de-duplication from Philippines:
Name + Mobile Number Example of 5 duplicate Name and Mobile Number combinations as found by CDQ: Name: Mohammad Kasim Mobile: +91-98336-90611 Name: Mohd. Kasim Mobile: 0091 98 33 69 06 11 Name: Mhd. Kasim Mobile: (9833) 690-611 Name: Md. Kasim Mobile: 0-98336-90611 Name: Muhammad Kasim Mobile: 9 8 3 3 6 9 0 6 1 1 Name + Date of Birth Example of 4 duplicate Person's Name and Company Name combinations as found by CDQ: Person's Name: Narendra Bajpayee Date of Birth: 15/11/1984 Person's Name: Narindir Bajpayee Date of Birth: 11-15-1984 Person's Name: Narender Bejpeyee Date of Birth: 15.11.84 Person's Name: Nariinder Baajpayii Date of Birth: 1984, novembr 15 Name + Company Example of 4 duplicate combinations of Person's and Company Names as found by CDQ: Person's Name: Sanjiv Kumar Company's Name: HPE India Private Limited Person's Name: Sanjeve Kumarr Company's Name: HPE India Private Ltd. Person's Name: Sanjeev Qumar Company's Name: HPE Pvt. Ltd Person's Name: Sanjive Koomar Company's Name: HPE Limited Website URL CDQ groups different Website URLs which refer to the same page in a single cluster. Here's an example of such a group:
Frequently Discussed TopicsOn location of hosted data CDQ's computational servers run on AWS Singapore and they are different from the servers where databases are kept. Our compute servers are fixed, but the database could reside in following 3 configurations - 1) Data on Contactous' Servers - Here, we create a separate environment for customer's data on one of our AWS Singapore instance. This is a good option if the data is of low volume or for a pilot project. This option is also used by our customers as a pre-CRM space, to scrub and clean the data before transferring it to other systems. 2) Data on Customer's own AWS Instance - We recommend this option as it is fast to setup and gives our customers assurance as the database access is managed by them. We help to set the system and establish the API access, after which the full control of database is with customer. 3) Data on Customer's own data center - This on-premise database location is possible. The setup is like in #2. Co-ordination and testing usually takes more time than #2. Security of application and platform Contactous' CDQ has 100% SaaS architecture, and is hosted on AWS Singapore. Compliance certificates are available at: https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/programs/ Entire application of Contactous (including all web services) are at https://web.contactous.com/. All external accesses to our platform are protected by the TLS 1.2 – HTTPS protocol. Strong encryption algorithms (AES 128 GCM) are used. Validated by SSLLabs (rated A). The risk of data being intercepted by a third party during transmission is minimal. Validate at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=web.contactous.com Every instance used by a customer runs a separate set of programs isolated from others. We are listed on Application Exchange of Salesforce and Microsoft - both of which have the highest level of security standards that we comply to. Check: https://itunes.apple.com/sg/app/contactous/id1161332503?mt=8 and https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.contactous&hl=en De-duplication speed and data volume CDQ has been designed to give fast results of de-duplication. In our sample database with over 2 million records, the duplicate pattern is found within a second. This speed has enabled our customers to use the system in real-time. When the records are read by CDQ, they get indexed in multiple ways through its complex algorithms. For smaller number of records like a couple of thousands, this indexing takes place automatically. When large datasets are imported, the indexing can be manually triggered. Large datasets can be uploaded into CDQ as CSV files. It is frequent for our customers to upload datasets of half million records as CSVs. In case there is a very large database of several million records that need to be indexed, our consultants can help to ensure that data upload is done successfully. Algorithms in use and customization The algorithms used for de-duplication and entity resolution within CDQ have the foundation of proven data matching frameworks, but have been developed from scratch. These algorithms heavily use fuzzy logic and other probabilistic methods to arrive at decisions. A big emphasis has been on the quality of output, which will remain as the guiding principle in future. The algorithms in current version of CDQ have been proven after running on millions of actual records. Our algorithms give 3 types of results: 1) Exact - The output is a result of direct match and this functionality can be compared to de-duplication by many CRMs. 2) Fuzzy - Based on our own AI based algorithms. This is probabilistic as compared to Exact match, which is deterministic. Then there is 3) Smart match - It shows results where our confidence level is very high and is a combination of deterministic and probabilistic approaches. On Pricing CDQ follows a yearly subscription model and its pricing is based on number of records that are stored or indexed by the application. There is no setup cost if the database is kept on Contactous' own servers. However, there is a one-time setup charge for a separate user's own AWS instance or on-premise database. Consulting services are charged separately, if taken. There are no other charges. Consulting services and partners 8 out of 10 users of CDQ are using it the way it is designed. All frequent combinations of de-duplication keys have been programmed in the system, which are used across industries in both B2C and B2B configurations. Creation of data dictionary too is always handled by users themselves, due to its simplicity. Still, there are 7 areas where our services have been asked, for more specialized tasks. 1) Creation of special de-duplication criteria 2) Implementation of user's own de-duplication algorithm 3) Custom logic of entity resolution methods 4) Special logic to merge duplicate records 5) Large data scrubbing and readiness 6) Extraction programs for unstructured data 7) Consulting services on data ETL Our experienced consultants and network of partners are available for such tasks. With proper Non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements in place, our team is ready to work with our user's on such requirements. |